| 特性 | BFS | DFS |
|---|---|---|
| 遍历顺序 | 层级顺序(广度优先) | 深度优先(前序/中序/后序) |
| 数据结构 | 队列(Queue) | 栈(Stack)或递归 |
| 适用场景 | 最短路径、社交网络好友推荐 | 拓扑排序、连通性检测、回溯问题 |
| 空间复杂度 | 较高(存储层级节点) | 较低(仅存储当前路径) |
拿二叉树的创建来举例,其中层序遍历是bfs,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历都是dfs
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
//定义二叉树节点类
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode (int val){
this.val = val;
this.left =null;
this.right = null;
}
}
//定义二叉树类
public class BinaryTree {
private TreeNode root;
public BinaryTree(){
this.root = null;
}
//插入节点
public void insert(int val){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
if(this.root == null){
this.root = node;
return;
}
//采用层级遍历插入节点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(this.root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
if(temp.left == null){
temp.left = node;
return;
}else{
queue.add(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right == null){
temp.right = node;
}else{
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
//前序遍历(根—左—右)
public void preOrder(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
System.out.println(root.val+" ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//中序遍历(左—根—右)
// 中序遍历(左 -> 根 -> 右)
public void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
// 后序遍历(左 -> 右 -> 根)
public void postOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.val + " ");
}
// 层级遍历(广度优先)
public void levelOrder() {
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(current.val + " ");
if (current.left != null) queue.add(current.left);
if (current.right != null) queue.add(current.right);
}
}
// 获取根节点
public TreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
}
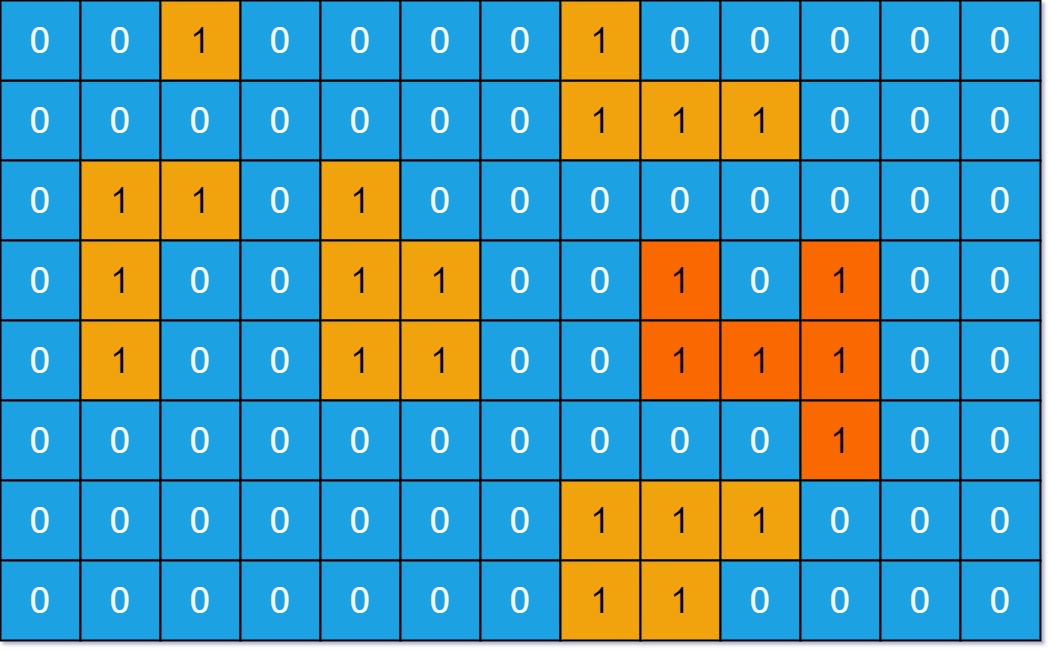
二维矩阵的层级遍历dfs和二叉树差不多,用于判断矩阵中岛屿相关的算法题
// 二维矩阵DFS遍历框架(含障碍物判断)
void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, boolean[][] visited) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
// 1. 边界检查
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n) {
return;
}
// 2. 跳过已访问或障碍物
if (visited[i][j] || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return;
}
// 3. 标记当前节点为已访问
visited[i][j] = true;
// 4. 递归访问四个方向(上、下、左、右)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j, visited); // 上
dfs(grid, i + 1, j, visited); // 下
dfs(grid, i, j - 1, visited); // 左
dfs(grid, i, j + 1, visited); // 右
}